Each IP camera is planned for video surveillance, until now, it explains different tasks. It is important to know under what situation what information of what quality the IP camera will transmit.
This article does not cover multi-sensor, PTZ, and panoramic IP cameras, but most of what has been said applies to them.
IP Camera Buying Guide: How to Choose an IP Camera?
- Choosing an IP Camera Lens
- Selecting an IP Camera Matrix
- IP camera resolution selection
- Outdoor IP cameras
- IR filter
- Backlight
- Audio
- Form factor
- Light control features
- Compression
- Broadcast speed
- Embedded analytics
- Additional functionality

Table of Contents
ToggleChoosing an IP Camera Lens
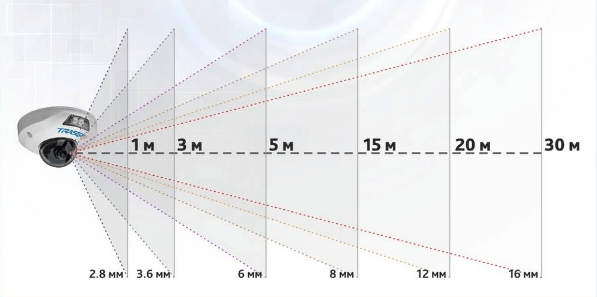
One of the most important parameters when choosing an IP camera is the angular field of the lens, the basis for determining the number of cameras and their mounting locations. This is the area visible to the lens, coverage. Viewing angles – horizontal, vertical, diagonal – are directly related to the focal length.
The focal length is fixed and variable; zoom lenses are motorized and manually controlled. A “manual” zoom lens greatly facilitates installation, and the distance itself is such that fixed lenses, such as 13.5mm, do not exist.
Motorized lens – for constant monitoring with the need to zoom in frequently

You will need an IP camera equipped with an IR-corrected lens for round-the-clock video surveillance with IR illumination as an additional light source. Visible light is focused at one point, and infrared rays are focused at another. If the focus is not shifted, the picture will be blurry, muddy – defocused.
IR correction in the lens is just a shift in focus. In the documents, IR correction is not always indicated, although it is present – check this point with the seller.
Selecting an IP Camera Matrix
The matrix collects the image from the lens and transfers it into a digital stream. The picture quality depends on the sensitivity of the matrix. Sensitivity is shown in lux (lx). Lux is the derivative of one lumen (luminous flux meter) per square meter.
The parameter indicates the minimum amount of light required to form an image – 0.1 ~ 0.9 lux, 0.01 ~ 0.09 lux, 0.001 ~ 0.009 lux. The more zeros after the dot, the more sensitive the matrix, the better the picture, and the longer the IP camera does not switch to black-and-white mode. A sensor with a sensitivity of 0.001 ~ 0.005 lux produces a better image and is capable of forming color video in the light of street lamps – if the lens aperture does not interfere with this.
An aperture is a relative opening that allows light to pass through. The lesser the number, the more light will go into the matrix. The aperture of a lens with an aperture of F / 1.2 is higher than with F / 2.0 – the aperture is larger, and more light passes through. There is little use for a sensitivity of 0.001 lux if this light is in the field of view, but does not pass to the matrix.
For an IP camera supplied without a lens, it is customary to indicate the sensitivity for optics with F / 1.2. Some manufacturers are tricky and indicate F / 1.2 when the camera is equipped with an F / 2.0 lens. Actual sensitivity will be lower than indicated. In addition, manufacturers measure it differently – in different conditions, with a different lens. How to choose an IP camera with good sensitivity?
Pay notice to the size of the matrix. The larger the sensor, the higher the sensitivity in reality- 4 is less than 1/2.8. The lower the noise, the fewer interpixel insulating elements there are on a small matrix, which increases heating and worsens the signal-to-noise ratio.
It has no matrices that are too large: the only limitation is the cost.
Unfortunately, there is no universal recipe for choosing sensitivity. Experience helps, but if it is not there, it is better to contact specialists, ideally the manufacturer.
IP Camera Resolution Selection
Unreasonably high resolution is fashionable, but often unprofitable: you will have to pay not only for the IP camera itself but also for high network bandwidth, DVR processor power, terabytes of hard drives, and equipment depreciation. In addition, the higher the resolution, the lower the sensitivity of the matrix – simple arithmetic: more pixels, but the same amount of light, less light for each pixel.
Choose the resolution depending on the tasks and shooting conditions. If you do not need a lot of detail, 2 megapixels will do – the resolution is sufficient for solving most tasks.
In some cases, even two megapixels are not needed.
Examples:
- A high-definition IP camera is installed at the entrance to the office. It captures all incoming. In the corridor, already fixed objects move – their movement is important, and detailing is no longer needed. Enough IP camera with a resolution of 1 megapixel. The same applies to interior spaces.
- An IP camera with a resolution of 2 megapixels is installed at the entrance to an apartment or house to capture visitors, but in the room itself, high resolution is needed only if you need to know whether the child is reading fiction or a textbook. In other cases, who is moving is already known – a cat or a nanny. 1 MP is enough.
High Resolution Needed
- in large open spaces of squares, halls, stadiums, stations, and airports – for shooting at long distances with the subsequent approximation of fragments;
- if necessary, often scale the picture – zoom in on certain areas;
- to clearly distinguish details, such as denominations and numbers of banknotes, car numbers at a great distance, etc.
In an inexpensive camera, high resolution will play the role of a disservice – a cheap processor is not able to process so many pixels, the pixel size of a small matrix is negligible and therefore it gets a minimum of light, and the picture is blurry – other things being equal, its quality is much worse than the quality of a picture with a resolution of 2 Mp.
Best Outdoor IP Camera
If you need an IP camera to work outdoors, pay attention not only to operating temperatures – they are low for unheated premises but also to protection (choose according to the task):
- From moisture and dust (without this, the IP camera is not outdoor): IP54 – the dust-proof device with splash protection, IP66 – dust-proof equipment with protection against jets under pressure, IP67 – short-term immersion in water to a depth of 1 m is permissible, IP68 – IP – the chamber will work in submerged (≤ 1 m) state up to 30 min.
- Corrosion Resistant: Minimum stainless steel enclosure, maximum NEMA 4X (protection against corrosion, windblown dust, and spray, pressurized hose water, frost damage).
- From mechanical influences – IK06 ~ IK10: IK06 – withstands a load drop of 500 g from a height of 20 cm, IK07 – 500 g from 40 cm, IK08 – 1.7 kg from 29.5 cm, IK09 – 5 kg from 20 cm, IK10 – 5 kg from 40 cm.
- From explosion – ATEX and IECEx; such IP cameras are designed for gas pipelines, oil refineries, chemical plants, etc.
There are no tricks in the protected characteristics, with the exception of vandal resistance. All standards have long been developed, described, and are in effect: protection is either there or not.
As for vandal protection, there is a catch on cheap models: the dome withstands a blow, but the filling crumbles and the camera does not work.
IR filter
Matrix IP cameras are sensitive to visible and infrared light. Rays of the infrared range distort color reproduction and spoil the image – purple spots appear on the picture, covering fragments of the frame.
To prevent this from happening, use an IR filter – ICR (Infrared Cut filter mechanically Removable; mechanically shifted infrared filter) or electronic. For night video surveillance, IP cameras operate in day/night mode – when there is a lack of light, they switch to black-and-white shooting mode.
- The mechanical IR filter is a plate with refracting IR rays, installed in front of the matrix, and equipped with a bias drive. In the dark, the filter is moved to the side so that the sensor’s sensitivity is increased, the backlight can work. The filter receives a shift signal from a photo sensor, which automatically controls not only the filter but also the backlight.
- Electronic IR filter – deposition directly on the matrix, which does not transmit IR rays in any shooting mode. In b / w, such cameras go – this gives a slight improvement in the picture, but the IR illumination is useless.
IR illumination
The greater the range of the backlight, the better – the wrong thesis: the backlight requires illumination of the observation area – no more. Long-range illumination – a directional beam that illuminates a narrow sector, and not the entire area. A lens with a focal length of 2.8 mm does not need such illumination, because the object of observation is close.
Please note – in the dark, the field of view will be twice as narrow. Equally, the quality of the picture will decrease, since the rays of the infrared range are perfectly reflected from rain, snow, dust suspension, midges, and other things.
The nuance of IR illumination with a long-range is the illumination of nearby objects. The problem is solved by adaptability: the processor receives data from the sensor about the distance to the object and proportionally changes the power of the diodes. When choosing an IP camera with a “long” backlight, make sure that the latter is adaptable – Smart will be written in the datasheet.
In summer, in hot regions, it makes sense to use IP cameras without IR illumination – with a separate spotlight. The built-in backlight diodes heat up, coupled with high air temperature, which creates unnecessary unplanned noise.
Audio in IP camera
If it is important not only to see but also to hear what is happening, you need an IP camera with a microphone. To organize a two-way voice message, you will need a speaker. Microphones are installed in many models, but the installation location often does not allow for legible recording – in such cases, an external microphone is connected to the IP camera (an audio input is required).
Form factor
The most popular dome and cylindrical IP cameras. Cylindrical IP cameras are often equipped with telephoto lenses, including motorized ones – the very shape of the body contributes to this. Basically, “cylinders” are placed on roads, entrances, and entrances with a high camera location, and large spaces (stadiums, train stations, airports, etc.).
Dome IP cameras can be mounted in places of direct access – low ceilings, walls, and so on, places that are not within the sight of security guards. The body shape is the most resistant to mechanical stress. “Domes” are universal – they are suitable for any object, but they are most relevant in parking lots, in low corridors, at entrances, and wherever you can reach the camera.
Vandal resistance as a parameter is also present in the cylinders, but the swivel bracket negates the advantage – an attacker just needs to turn the camera in the other direction. The same applies to the form factor “Sphere” (the video module is spinning) and Cube. In an IP camera with analytics, an anti-sabotage function, and specific detection of a change in the field of view and impact detection, an alarm signal will be sent to the system, but until it is responded to, time will pass, often quite sufficient to commit a crime. Such cameras are used in office rooms, residential premises, school classrooms, and other similar facilities.
Standing apart are IP cameras in the Box form factor. They are not equipped with lenses, leaving the choice of optimal optics to the designer. They are not outdoors – thermal casings are needed for external installation. This is professional equipment – it is often used to recognize face entrances, and license plates at entrances.
Selecting anti-light functions
Light does not take into account the need for video surveillance, especially on the street – shadows change location, darken entire areas, and the sun moves, illuminating different areas depending on the time of day. Professional photographers love backlight, but even they find it difficult to work with it, and for video surveillance, this is a serious complication that destroys the information content of the picture: against a bright background, only the silhouette of the object is visible, without details. There are software and hardware solutions to deal with different-contrast lighting or its consequences:
- DWDR – digital post-processing, selectively increasing the brightness of dark areas of the scene and darkening too light areas.
- WDR indicating the range up to 110 dB is a hardware function; the processor selects the optimal shutter speed within the specified decibel interval (the dynamic range of the matrix). A lot can be achieved with shutter speed – the waterfall looks like drops on a short one and a bright light stream on a long one.
- WDR with an indication of the range from 120 dB is a hardware function (usually referred to as Real or True), not only the choice of shutter speed but also the creation of several frames (Double Scan, Quadro Scan) with different exposures, their subsequent assessment of the brightness of various areas and summation in one is balanced.
- WDR with an indication of the range from 120 dB is a hardware function implemented directly in the matrix; an exposure metering system located around each pixel: for pixels where there is a lot of light, the shutter speed is short, where there is little – long.
There is also BLC, which corrects a specifically bright background, and HLC, which fights against local flare (headlights, lanterns) by masking or dimming.
HLC is local, DWDR and BLC give a low effect, per-pixel metering is medium, and multiple scans are high (there are no shadows even where they should be), but not everything is so simple.
Multiple scan WDR is not suitable for high-speed object surveillance and IP cameras with analytics. Example: live video frame rate – 25 frames per second, city car speed – 60 km/h; in a minute the car will travel a kilometer, in a second – 16.6 meters, in 1/25 of a second – 66.6 cm, but we take two frames, which means that the car will travel 30 cm between frames, and this will generate artifacts in the image. If the speed is high, a double display of the car is likely.
Arti facts also do not contribute to the analysis of the flow – it is not clear whether the runner crossed the line or not, entered the area, or left it, it is impossible to correctly recognize the card number when the numbers overlap, and so on.
For video surveillance in areas with fast-moving objects, Real WDR is not suitable, it must be turned off. But then why this function? It is better to give preference to pixel-by-pixel metering or DWDR.
Compression
H.264, and H.265 codecs are responsible for compression. The H.265 standard is most effective at high resolution – at 2 megapixels it does not realize the advantages (there are not enough pixels for many 64 by 64 blocks). In most cases, H.264 is sufficient. Now it is fashionable to implement the entire set, including the so-called smart codecs, According to the principle the more the better, but this is superfluous – do not forget that all standards are paid: the more there are in the camera, the more expensive it is.
Smart codecs are H.264+, H.265+ (Hikvision), ZipStream (Axis), and WiseStream (Hanwha Techwin), which increase the efficiency of H.264, H.265, manufacturers’ development, based on the pre-compression of static frames used in as a base.
Broadcast Speed
The lower the recording speed, the faster objects on the monitor move during playback. Charlie Chaplin didn’t really mince—it was the cinematography that was slow.
It is believed that 25 fps is always necessary. But the total need is far-fetched: real-time video is needed where there is constant movement, and to record what is happening at the emergency exit, dormant reception, on the roof, some parts of the perimeter, and most of the interior of the same office, high speed is not needed – 15 fps is enough, and you can save on bitrate.
On the tracks, on the contrary, 25 frames per second are not enough – 50-60 fps are needed there so that fast-moving cars can be seen on smooth scrolling.
Embedded Analytics
The software motion detector that has become familiar is already analytics (in fact, it does not detect motion as such, but analyzes the image for changes), and it frees the operator from endless viewing of monitors, saves archival space, time to view records, reduces network load, because that with the appropriate settings, the IP camera starts recording only on a signal from the detector.
Today, with the help of analytics built into the camera, many tasks are solved. Among the analytical functions are the detection of the intersection of a virtual line, abandoned or missing objects, movement with the classification of objects by size, speed, and direction, entering and leaving the area, intrusion into the zone, fog, people, cars, bicycles, counting visitors, sound detection, violations (excess/underestimation) of the sound threshold, lens barrier, changes in the field of view, picture substitution, sound classification, behavior analysis (falling, loitering, etc.) and a range of highly specialized functions.
Technologies are developing at an enviable rate, and in the future, the list of analytical capabilities of IP cameras will expand, including in the direction of neural network solutions.
Additional Functionality
- If the network is unstable, there are disconnections, Choose cameras that support an internal archive with recording to an SD card or flash drive – you will not lose information. It is necessary that the registrar or the cloud support the work with the archive of the IP camera, including the resume. The technology also saves from power outages if the system has a UPS: the DVR is more powerful equipment, the power source will not last long, and the power consumption of the cameras is low – it can work for a couple of hours.
- If you need an IP camera in the corridor, between racks, and the like, choose the appropriate vertical display mode – it is indicated in the specifications. The blind zone will be much smaller, the image will be better. You can’t just flip the image – the picture will lie on its side. Need hardware support for corridor mode and vertical resolution.
- If the power supply is not available at the location where the IP camera is installed, choose a model that supports power over twisted pair (PoE technology) – from a registrar or a switch. Otherwise, there is no need to overpay for PoE.
- When choosing an IP camera with a motorized lens, auto iris, and focus, pay attention to the locking feature – there is nothing good about floating focus and aperture.
- In places with a possibility of vibration (road, workshop, etc.), buy IP cameras with digital image stabilization (DIS), leveling the effects of shaking (blur). Some manufacturers enhance the function in hardware, completing the IP camera with a gyroscope, and DIS turns on at the slightest shift.
- If you need an IP camera to monitor an area with heavy traffic or choose a model with analytics, buy with 3D DNR spatial noise reduction. For quiet areas, 2D DNR is sufficient.
IP Camera Buying Guide Tips
- Choose a camera not by price, but by functionality – so that the equipment solves the tasks. Budget budget, but the preference for cheap is a great way to drain this budget.
- If even after reading the article it is difficult to understand the characteristics, ask to see an example of recording from a particular camera. A conscientious and interested manufacturer will not refuse.
- Do not buy IP cameras without taking into account the parameters of the DVR: equipment compatibility is a must.
- When buying wireless IP cameras, be aware of physical obstacles – partitions and the like will reduce the data transfer distance.
- According to statistics, installers choose one type of IP camera, while users choose another. And often users are met with negative surprises. Contact a specialist if you are not sure about the correct choice of each characteristic.