When it comes to heating systems, understanding the different types of heat emitters is essential for making the right choice for your home or business. From traditional radiators to modern underfloor heating, each type has its own unique advantages and considerations.
In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss the various types of heat emitters available, explain how they work, and provide insights into their pros and cons. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the different options, helping you make an informed decision about your heating requirements. Check out also Mr. Heater Portable Buddy Heater for Outdoors.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Radiators: Efficient and Versatile Heat Emitters for Your Space
Radiators have long been a popular choice for heating systems, offering both functionality and aesthetic appeal. Whether you’re looking to warm up a cozy bedroom or a spacious living area, radiators provide an efficient way to distribute heat and maintain a comfortable environment.

Radiators come in various shapes and sizes, catering to different heating needs and interior design preferences. One common type is the panel radiator, which consists of a series of metal panels with fins or convectors inside. These panels increase the surface area, allowing for optimal heat transfer. Panel radiators are versatile and can be installed both horizontally and vertically, making them suitable for a wide range of spaces.

Buy From Amazon
Another type of radiator is the towel radiator, which combines functionality with luxury. These radiators are specifically designed to warm towels and provide a touch of elegance to bathrooms. Towel radiators come in different styles, including ladder-style and traditional column radiators, allowing you to choose one that complements your bathroom decor.

Buy From Amazon
Radiators work by utilizing convection, a process where heat is transferred through the movement of air. As the hot water flows through the radiator’s pipes, the metal panels heat up, causing the surrounding air to rise and create a convection current. This upward movement of warm air circulates throughout the room, gradually heating it to a comfortable temperature.
The efficiency of radiators largely depends on several factors, such as the size and design of the radiator, insulation levels in the room, and the boiler’s performance. Modern radiators are designed to maximize heat output and minimize heat loss, ensuring efficient heating. Additionally, thermostatic radiator valves (TRVs) can be installed to regulate the temperature of individual radiators, allowing for zoned heating and energy savings.
Let’s now explore the pros and cons of using radiators for heating:
Pros:
- Effective Heat Distribution: Radiators provide rapid heat distribution, quickly warming up a room and maintaining a consistent temperature.
- Versatility: With various sizes and styles available, radiators can be installed in any room, including bedrooms, living rooms, kitchens, and bathrooms.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Radiators come in a wide range of designs, from sleek and modern to classic and ornate, allowing you to choose one that enhances your interior decor.
- Reliability: Radiators have a long lifespan and require minimal maintenance, making them a reliable heating solution.
- Cost-Effective: Radiators are generally more affordable compared to other heating systems, making them an economical choice for homeowners.
Cons:
- Space Occupancy: Radiators can take up wall space, potentially limiting furniture placement and room layout options.
- Uneven Heat Distribution: In larger spaces, it may be challenging to achieve consistent heat distribution throughout the room, leading to temperature variations.
- Heat Loss: Radiators can lose heat through walls and windows, especially if the room lacks proper insulation.
- Lack of Control: Without additional controls, radiators may not offer precise temperature control in each room, resulting in potential energy wastage.
In conclusion, radiators are a popular choice for heating systems, providing effective heat distribution and aesthetic appeal. With options like panel radiators and towel radiators, you can find the perfect match for your space and personal preferences. While radiators offer numerous advantages, it’s important to consider potential limitations, such as uneven heat distribution and heat loss.
By understanding the pros and cons, you can make an informed decision and enjoy the warmth and comfort that radiators bring to your home.
2. Underfloor Heating: Modern Comfort and Efficiency at Your Feet
Underfloor heating is a revolutionary method of heating that offers both comfort and energy efficiency. With this system, warmth is evenly distributed from the floor, creating a cozy and comfortable environment in your home.

Underfloor heating is a modern and efficient heat emitter that has gained popularity in recent years. It involves installing a network of pipes or electric heating elements beneath the floor surface, which then radiate heat upwards. This radiant heat warms the room from the ground up, eliminating cold spots and providing a more even distribution of heat.
There are two main types of underfloor heating systems: electric and water-based (hydronic). Electric systems use electric heating elements that are installed beneath the floor, while water-based systems circulate warm water through a network of pipes. Both types have their advantages and considerations.
1. Electric Underfloor Heating Systems
Electric underfloor heating systems are easy to install and are typically used in smaller areas, such as bathrooms kitchens, and bedrooms. They are controlled by a thermostat, allowing precise temperature regulation for each room. Electric systems also have a faster response time, providing warmth quickly when needed.

Buy From Amazon
2. Water-Based Underfloor Heating Systems
Water-based underfloor heating systems use a network of pipes that circulate warm water supplied by a boiler or heat pump. These systems are more commonly used in larger areas and can be installed in both new constructions and retrofit projects. Water-based systems offer greater energy efficiency and can be integrated with other heating sources, such as solar thermal or geothermal systems.
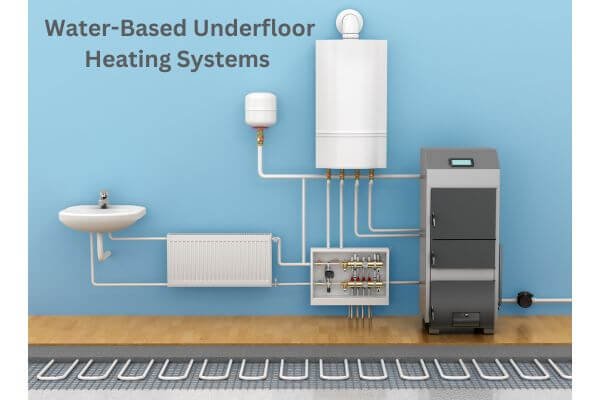

The installation process of underfloor heating depends on various factors, including the type of system and the existing flooring. For new constructions, the installation process involves laying the pipes or heating elements on insulation and covering them with a screed or self-leveling compound. Retrofit installations require removing the existing flooring, installing the heating system, and then replacing the floor covering.
When considering underfloor heating, there are several considerations to keep in mind. The type of flooring is crucial, as some materials, such as tile, stone, or laminate, work well with underfloor heating, while others, like carpet, may impede heat transfer.
Insulation is also essential to minimize heat loss and improve the efficiency of the system. Additionally, it’s important to calculate the heat load of the room accurately to ensure that the underfloor heating system is appropriately sized.
Underfloor Heating offers Numerous Benefits Compared to Traditional Heating Options:
- Comfort and Even Heat Distribution: Underfloor heating provides consistent and comfortable warmth throughout the room, with no cold spots or drafts.
- Energy Efficiency: With underfloor heating, heat is evenly distributed at a lower temperature, resulting in energy savings and reduced heating costs.
- Design Freedom: Underfloor heating eliminates the need for radiators, freeing up wall space and allowing for more flexibility in room layout and furniture placement.
- Silent Operation: Underfloor heating operates silently, without the noise associated with forced-air systems or radiators.
- Allergy-Friendly: Unlike forced-air systems that can circulate dust and allergens, underfloor heating minimizes air movement, creating a healthier indoor environment.
However, underfloor heating also has some drawbacks to consider:
- Initial Cost: Underfloor heating systems can have higher upfront costs compared to traditional heating systems, especially for water-based systems that require a boiler or heat pump.
- Installation Complexity: Installing underfloor heating may require professional assistance, particularly for retrofit projects or water-based systems.
- Response Time: Compared to radiators or forced-air systems, underfloor heating may have a slower response time, as the thermal mass of the floor takes time to heat up.
- Limited Zoning Control: Unless a sophisticated zoning system is implemented, it can be challenging to have precise temperature control in different areas or rooms. This may result in heating unused spaces and potentially wasting energy.
- Flooring Constraints: Underfloor heating is compatible with most types of flooring, but certain materials, such as thick carpets or hardwood, may require specific considerations and insulation to ensure efficient heat transfer.
Despite these drawbacks, underfloor heating remains a popular choice for homeowners seeking optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
In conclusion, underfloor heating offers a modern and efficient way to heat your home. Whether you choose an electric or water-based system, the benefits of underfloor heating, such as even heat distribution, energy efficiency, design freedom, and allergy-friendliness, make it an attractive option.
However, it’s important to consider factors like initial cost, installation complexity, response time, limited zoning control, and flooring constraints before deciding if underfloor heating is suitable for your specific needs and budget.
If you prioritize comfort, energy efficiency, and a sleek, clutter-free aesthetic, underfloor heating might be the perfect solution for you. Consult with professionals to assess your space, determine the most suitable system, and ensure proper installation. With underfloor heating, you can enjoy cozy warmth under your feet and create a comfortable living environment for years to come.
3. Convectors:
Versatile Heat Emitters for Efficient Heating
Convectors are a popular choice when it comes to heating systems, offering versatility and efficient heat distribution. These devices work by utilizing convection, a process that efficiently heats the air and creates a comfortable living space.

Buy From Amazon
Convectors are heat emitters that operate by circulating air across a heated surface, transferring warmth to the surrounding environment. They rely on convection currents, where cool air is drawn in from the bottom of the unit, heated, and then expelled through the top. This continuous circulation of air creates an efficient heat distribution and helps maintain a consistent temperature throughout the room.

Buy From Amazon
One of the key advantages of convectors is their versatility. They can be installed in various locations within a space, such as walls or baseboards, depending on the specific design and model. Wall-mounted convectors are often discreet and blend seamlessly with the room decor. On the other hand, baseboard convectors are installed along the base of walls and provide an unobtrusive heating solution.
Convectors come in different types, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Wall-mounted convectors are popular for their space-saving design and easy installation. They are typically mounted on the wall at a higher level, allowing for efficient heat distribution across the room.
Baseboard convectors, as the name suggests, are installed along the baseboard of walls, providing heating from a lower position. They are ideal for rooms with large windows or limited wall space.
Now, let’s delve into the advantages and disadvantages of using convectors for heating:
Advantages:
- Efficient Heat Distribution: Convectors effectively distribute heat across the room through convection currents, resulting in consistent warmth throughout the space.
- Rapid Heating Response: Convectors offer fast heating response times, allowing you to quickly warm up a room when needed.
- Versatile Installation Options: Convectors can be installed in various locations, such as walls or baseboards, providing flexibility in terms of placement and space utilization.
- Precise Temperature Control: Many convectors are equipped with thermostats or temperature control settings, allowing you to regulate the heat output and maintain a comfortable temperature.
- Design Flexibility: Convectors come in a range of styles and designs, offering options that can complement any interior decor.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Surface Area: Convectors have a relatively smaller surface area compared to other heat emitters, which may result in lower heat output in larger rooms or spaces.
- Air Movement and Dust Circulation: The convection process in convectors involves moving air, which can potentially circulate dust and allergens throughout the room.
- Noise Level: Some convectors may produce a gentle humming noise during operation, although advancements in technology have reduced this issue in modern models.
- Space Constraints: Convectors, especially baseboard models, may take up valuable wall or floor space, limiting furniture placement options.
Choosing the Right Heat Emitter: A Comprehensive Comparison and Considerations
When it comes to heating your home, selecting the right heat emitter is crucial for achieving optimal comfort and energy efficiency. Radiators, underfloor heating, and convectors are popular options, each with its own advantages and considerations.
Radiators
Radiators have long been a popular choice for heating systems. They offer effective heat distribution and come in a variety of styles and designs to suit different preferences. Radiators work by utilizing convection, where heated panels or columns warm the surrounding air, creating a comfortable environment.
Factors to consider when choosing radiators include cost, efficiency, installation requirements, and aesthetic appeal.
Cost: Radiators generally have a lower upfront cost compared to underfloor heating systems. They are relatively affordable to purchase and install.
Efficiency: Modern radiators are designed to maximize heat output and minimize heat loss. The efficiency of radiators can be further improved by using thermostatic radiator valves (TRVs) and ensuring proper insulation in the room.
Installation Requirements: Radiators require wall space for installation and connection to a central heating system. They are relatively easy to install, especially in existing buildings.
Aesthetic Appeal: Radiators offer a wide range of design options, from sleek and modern to traditional and ornate, allowing you to choose one that enhances your interior decor.
Underfloor Heating
Underfloor heating provides a luxurious and efficient heating solution. It works by radiating heat from the floor, creating a comfortable and even warmth throughout the room. There are electric and water-based (hydronic) underfloor heating systems available. Considerations for underfloor heating include cost, efficiency, installation requirements, and flooring compatibility.
Cost: Underfloor heating systems can have higher upfront costs compared to radiators. Water-based systems require a boiler or heat pump, increasing installation expenses.
Efficiency: Underfloor heating offers excellent energy efficiency, as it operates at lower temperatures and provides even heat distribution. It can be combined with renewable energy sources for further efficiency gains.
Installation Requirements: Installing underfloor heating requires careful planning and professional assistance. It is more suitable for new construction, but retrofit installations are also possible.
Flooring Compatibility: Different types of flooring have varying levels of compatibility with underfloor heating. Materials like tile, stone, and laminate work well, while thick carpets may impede heat transfer.
Convectors
Convectors are versatile heat emitters that rely on convection currents to distribute warmth. They can be wall-mounted or baseboard models. Considerations for convectors include cost, efficiency, installation requirements, and space constraints.
Cost: Convectors generally have moderate upfront costs, depending on the specific model and installation requirements.
Efficiency: Convectors offer efficient heat distribution through convection currents. They provide a rapid heating response and precise temperature control.
Installation Requirements: Convectors are relatively easy to install, and they can be placed on walls or baseboards, depending on the model. Baseboard convectors may take up floor space along walls.
Space Constraints: Convectors, especially baseboard models, can limit furniture placement options due to their positioning along walls.
Author Recommendations
When choosing a heat emitter, it’s important to consider factors such as cost, efficiency, installation requirements, and aesthetic preferences. Here are some recommendations based on different scenarios:
- If cost is a primary concern and you want a versatile option with various design choices, radiators can be a suitable choice.
- For those seeking luxurious comfort and energy efficiency, underfloor heating is an excellent option, especially for new constructions or projects where floor renovation is planned.
- If you prioritize rapid heating response, precise temperature control, and installation flexibility, convectors can be a great choice. They are particularly suitable for smaller spaces or rooms where wall or floor space is limited.
To optimize the performance of your chosen heat emitter, consider the following tips
1. Proper Insulation
Ensure that your walls, floors, and ceilings are well insulated to minimize heat loss and maximize the efficiency of your heating system. Good insulation helps retain warmth within the space.
2. Zoning and Temperature Control
Implement zoning controls, such as thermostats or programmable timers, to regulate the temperature in different areas of your home. This allows you to customize heating levels based on occupancy and preferences, resulting in energy savings.
3. Regular Maintenance
Keep your heat emitters clean and free from dust or debris to ensure efficient heat transfer. Periodically check for leaks, valve functionality, and air bleeds in radiator systems to maintain their performance.
4. Use Smart Technology
Consider integrating smart heating controls and devices to optimize energy usage. Smart thermostats can learn your heating patterns, adjust temperatures based on occupancy, and allow remote control through smartphone apps.
5. Combine Heating Systems
In some cases, combining different heat emitters can provide a balanced and efficient heating solution. For example, you can use underfloor heating as the primary source of heat in larger areas, while using radiators or convectors in smaller spaces or rooms where quick heating is desired.
Ultimately, the choice of heat emitter depends on your specific needs, budget, and preferences. Consider factors such as cost, efficiency, installation requirements, space availability, and aesthetic appeal. Consulting with professionals in the heating industry can provide valuable insights and help you make an informed decision.
Conclusion
Choosing the right heat emitter is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient space. By exploring the various types of heat emitters, including radiators, underfloor heating, and convectors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your needs and preferences.
Remember to consider factors such as cost, efficiency, and installation requirements when selecting the most suitable heat emitter for your home or business. Whether you opt for the classic appeal of radiators or the modern efficiency of underfloor heating, understanding the pros and cons of each option will guide you toward a heating system that ensures warmth and comfort all year round.
What are the three types of heat emitters?
Three types of heat emitters are currently on the market: dry, fluid, and ceramic. All of these, despite having the same purpose and being electrical, work differently:
1. Fluid thermal emitters: it is based on an electrical resistance that exchanges heat with a thermal fluid of low viscosity and neutral composition. This, in turn, transmits heat to the entire surface of the equipment and is used to heat the desired space.
2. Dry thermal emitters: use an electrical resistance as the previous one as heat production, the body of the thermal emitter, which is made of aluminum, absorbs this heat and is transmitted through the entire surface of the thermal emitter to heat the room in question
- Perfect Fit Soft Heat | Smart Heated Electric Mattress Pad with Safe & Warm Low Voltage Technology
3. Ceramic thermal emitters are made up of a ceramic element that accumulates heat. Ceramic heat-emitter bulbs are the ones that take the longest to reach the maximum temperature. Still, due to their high thermal inertia, they are the ones that maintain heat for the longest time.
8 Things to Know about Heat Emitters
1. The Efficiency of Thermal Emitters
Thermal emitters are quite efficient pieces of equipment. However, their efficiency depends a lot on the model we buy. On the other hand, it also depends on the user’s needs at home. Among them, we can distinguish the efficiency as follows:
- Fluid thermal emitters: the heating time of these types of equipment is greater, but they maintain the temperature for a longer time. Their ideal use is from 5 to 8 hours.
- Dry thermal emitters are the most economical equipment within the range of thermal emitters, and their ideal use is 1-5 hours.
- Ceramic heat emitters: These devices take the longest to heat up but remain hot the longest. They are recommended for installation and continuous use of more than 8 hours.
2. Consumption of Thermal Emitters
Can you save with a thermal emitter?
The truth is that with thermal emitters, you do not save money to a great extent. As its operation is based on the Joule effect, an electric radiator or thermal emitter consumes 1 KWh for each thermal KWh it produces (approx.). Therefore, if I install a 2 kW heating emitter, it will consume 2 kW of electricity.
- Smart Baseboard Heaters Household Floor Heating Electric Heaters Power-saving, Energy-saving Electric Radiator Heaters

Especially when we speak in economic terms, they cost the same as any other electric oil radiator. They heat the same at the same power and consume the same. Of course, many people say that the heat they provide is much more pleasant than that of an air conditioner.

3. The Average Price of Thermal Emitters
Thermal emitters are usually quite cheap since you can find a wide variety on the market, making the demand for a price much better. However, the price will be based on the power, brand, or type of emitter (either dry, fluid, or ceramic) that the equipment has. Below, we present the average price according to the type of issuer, based on the brands or equipment most in demand today:
- Fluid thermal emitters: The price of these devices ranges between 180 and 400, depending on the brand or power.
- Dry thermal emitters: Among the ten best-sellers of 2017, prices range between 105 and 220.
- Ceramic thermal emitters: The difference is not much concerning the others. You can find good models that range between 150 and 350.
We must clarify that the prices mentioned above are approximate since they can vary according to the demands that each person has or the number of square meters that are intended to be heated.
4. Cost of Heat Emitter
It has to do directly with its consumption, and in the same way, it is based on the power of the equipment that we have installed at home and the use that we give it. For the same reason, proper use is recommended without the need to have the heat emitter operating all day to minimize the costs generated. Thermal emitters, however, are usually heating equipment with which savings can be achieved compared to other traditional heating systems. Below, we give you a fairly detailed example of the expense you have with a thermal emitter:
| Variables | dry heat emitter | Fluid thermal emitter |
| Power | 5,0 KW | 5,0 KW |
| KW Gas cost | 0,117 | 0,117 |
| Consumption | 5 hours/day | 4 hours/day |
| Total KWh/dia | 25 kWh | 20 kWh |
| amount/day | 2,92 | 2,34 |
| 12 Hours of Operation | 5 hours of consumption | 4 hours of consumption |
| Consumption Month | 87,6 | 70,20 |
5. Installation of Heat Emitters
It is one of the most demanded heating systems since its installation only requires a small assembly. The assembly is simpler than it seems, and they also usually include an installation kit. You will only have to help yourself with a drill, a pencil, and a screwdriver.
We give you some recommendations on where to place it:
- In addition to the kit, the heat emitters usually come with a template, so you know where you have to drill the holes.
- They must be installed near a plug since they are connected to the electrical current.
- The distance from the emitter to the ground is measured, and when the measurements are clear, it will be time to place the template on the wall.
- We make marks where the holes are made with the drill.
- In each of the holes, we will put some plugs and place the pegs with the supports. The issuer will go over them.
This is an installation that anyone can do with a bit of experience. If this is not the case, we recommend that you go to a professional.
6. Maintenance and Repair of Heat Emitters
One of the great advantages of this heating equipment is that they do not require any maintenance, except for some cleaning to prevent dust from accumulating in it. When working with an electrical source, the thermal emitters can present faults that we will have to repair. However, the repair of the thermal emitters is quite simple.
In most cases, it is only a question of some resistance or plate within the same system. But apart from the repairs that may occur, we do not have to call or hire specialized companies to carry out maintenance as is often the case with other heating equipment, such as a gas or pellet boiler, etc
7. Spare Parts of Thermal Emitters
Thermal emitters are characterized by being efficient equipment having a long useful life, and not requiring frequent replacement of parts or demanding repairs. The spare parts in this type of equipment are not entirely recommended for the cheapest ones. It is more profitable to replace them with a new one in many cases since they are quite cheap.
Even so, there is also the possibility of asking for the budget of the technician and the parts if we should carry out a replacement and later evaluate whether it is profitable or not. If a replacement has to be made, however simple it may be, it must be carried out by a specialist and, in this way, avoid any subsequent problem or a total failure of the equipment.
8. Aspects that We Must Take into Account When Choosing the Best Thermal Emitter.
| Aspects | Characteristics |
| Power | 80-100 w/m², and in rooms larger than 15 m², more than 2 emitters are necessary to better distribute the heat. |
| Operating time | For the operation of 1 hour a day with rapid heating, we will use a dry emitter. For use between 5-8 hours, it is better to opt for a fluid emitter. For uses of more than 8 hours, we opted for a ceramic emitter. |
| Isolation | Have insulation in walls, ceilings, and windows to better keep the heat. |
| programming | Control temperature variations and daily consumption. |
| climatic zone | The temperature of the geographical area influences the power. Colder areas have more power. |
Thermal emitters in the USA
Many people in the USA decide to install thermal emitters in the home, either as main or support heating systems. In most cases, this type of installation is because the equipment is quite cheap about other heating systems. After all, it does not require a large installation and is almost completely maintenance-free.
According to a study carried out by FEGECA on thermal emitters and underfloor air conditioning systems, it reflects an increase of 5.38% in sales of radiators in Spain, with more than 891,000 units sold in 2017. Whether it is a new work or a replacement, especially the segments of aluminum, bathroom, and steel sheet panels have grown the most
More Related Articles